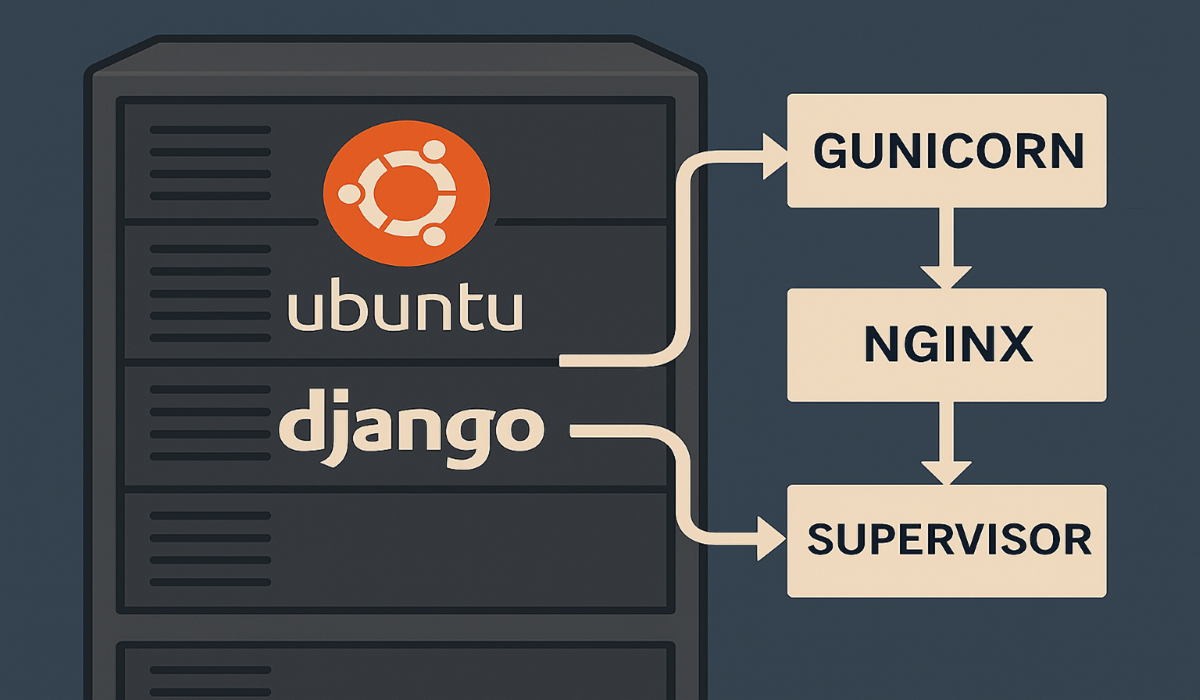
Why This Stack for Django Deployment?
This production-ready setup combines the best tools for Django deployment:
- Gunicorn: A robust WSGI HTTP server for Python applications
- Nginx: High-performance web server and reverse proxy
- Supervisor: Process control system to keep your app running
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu server (18.04/20.04/22.04)
- Python 3.6+ installed
- Django project ready for deployment
- Basic familiarity with Linux commands
Step 1: Install Required Packages
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-dev libpq-dev nginx supervisorStep 2: Set Up Virtual Environment
python3 -m venv myenv
source myenv/bin/activate
pip install django gunicorn psycopg2-binaryStep 3: Configure Gunicorn
Test Gunicorn can serve your Django project:
gunicorn --bind 0.0.0.0:8000 myproject.wsgi:applicationCreate a Gunicorn systemd service file at /etc/systemd/system/gunicorn.service:
[Unit]
Description=gunicorn daemon
After=network.target
[Service]
User=www-data
Group=www-data
WorkingDirectory=/path/to/your/project
ExecStart=/path/to/venv/bin/gunicorn --access-logfile - --workers 3 --bind unix:/path/to/your/project/myproject.sock myproject.wsgi:application
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetThen enable and start the service:
sudo systemctl start gunicorn
sudo systemctl enable gunicornStep 4: Configure Nginx
Create an Nginx config file at /etc/nginx/sites-available/myproject:
server {
listen 80;
server_name yourdomain.com;
location = /favicon.ico { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
location /static/ {
root /path/to/your/project;
}
location / {
include proxy_params;
proxy_pass http://unix:/path/to/your/project/myproject.sock;
}
}Enable the configuration and test Nginx:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/myproject /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginxStep 5: Set Up Supervisor
Create a Supervisor config file at /etc/supervisor/conf.d/gunicorn.conf:
[program:gunicorn]
command=/path/to/venv/bin/gunicorn --workers 3 --bind unix:/path/to/your/project/myproject.sock myproject.wsgi:application
directory=/path/to/your/project
user=www-data
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stderr_logfile=/var/log/gunicorn.err.log
stdout_logfile=/var/log/gunicorn.out.logUpdate Supervisor and start your application:
sudo supervisorctl reread
sudo supervisorctl update
sudo supervisorctl start gunicornSecurity Considerations
- Set up SSL/TLS with Let's Encrypt
- Configure proper file permissions
- Use environment variables for sensitive data
- Implement proper firewall rules (UFW)
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 502 Bad Gateway: Check Gunicorn is running and socket permissions
- Static files not loading: Verify Nginx has proper access to static directory
- Supervisor not starting: Check log files for specific errors
Optimizing Your Setup
- Adjust Gunicorn worker count (typically 2-4 x CPU cores)
- Implement database connection pooling
- Set up proper caching with Redis or Memcached
- Configure log rotation
Conclusion: Production-Ready Django Deployment
You now have a robust Django deployment stack that can handle real-world traffic. This setup provides the foundation you can build upon with additional optimizations as your application grows.
Next steps: Monitor your application's performance, set up automated backups, and consider implementing CI/CD pipelines for smoother deployments.